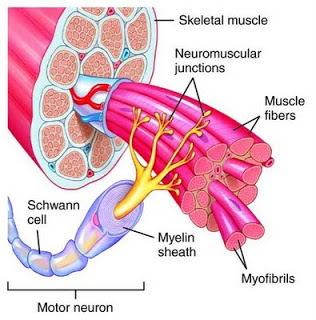
I’m sure you’ve been at an exercise class and have been told, or yelled at to “tighten that stomach!” or “squeeze those glutes!” So it is logical that a common question I’ve been asked is “why are you working out my tight muscles? Aren’t tight muscles a good thing?”
There is a difference between a tight muscle and a strong muscle. A muscle that is tight has too much tone when it is at rest and strength is the ability to of the nervous system to recruit neurons in the muscle fibers.
Strength is really cool to me and is probably a term that means different things to different people. Strength is defined as the maximal force a muscle can generate against a given force. There are different types of strength: maximum strength, strength endurance, and power.
Strength Is Not What You Think It Is!
You may think that strength comes from the size of the muscle but not really. Muscle strength comes from the ability of the nervous system to recruit neurons in the muscle fibers.
The muscle is made up of thousands of muscle fibers or cells. Within 1 muscle cell there are many neurons connected to it. So, in one muscle there are thousands of neurons in one muscle. The more neurons that fire the more the muscle works.
This is why muscle size is thought to be the main component of strength because the bigger the muscle means more muscle fibers and more motor neurons which means more of the muscle will work.
What Smart Strength Experts Know
With everyday movements not all of the neurons fire because you don’t need them all. But for extreme strength you do. Smart strength experts know this little secret. The more motor neurons that fire the more muscle fibers that contract, the more of the muscle that works. Imagine if you could get all of your motor neurons to fire? Really, if you can recruit the muscles well you could get the same effect without weights and some strength experts recommend pre-tensing the muscles before lifting.
However, in some ways strength isn’t all about muscle contraction. Consider power. Power is strength plus speed. So that’s the ability of the muscle to produce force plus speed which in some ways is an oppossite concept. When a muscle or muscles contract it will slow a movement down. So power requires the special ability of relaxing muscles at the right moment and tightening at the right moment.
Did you ever wonder why Tai Chi masters practice their movements slowly? Many people today think that it was more for a practice of health. It probably had more to do with when they practiced slowly they could focus on the relaxation of the arm or legs and focus on the precise point of contraction. They knew that when you practiced fast and hard all the time you would miss the small intricacies of tightening plus relaxation which equals power!
Tight Muscles Impede Sports Performance
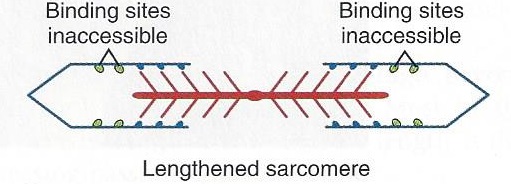
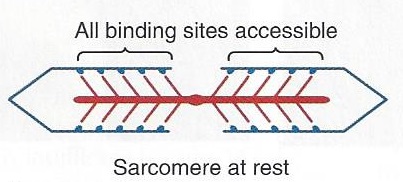 So, how do tight muscles impede sports performance? When a muscle contracts tiny globular arms in the cell pull sarcomeres together and when enough sarcomeres are pulled together the muscle is shortened.
So, how do tight muscles impede sports performance? When a muscle contracts tiny globular arms in the cell pull sarcomeres together and when enough sarcomeres are pulled together the muscle is shortened.
But when a muscle is already tight while at rest actin sites are too close together and the muscle has nothing to pull on. It will have a more difficult time producing a contraction.
And if a muscle on one side is tight that means another is lengthened. When a muscle is lengthened the sarcomeres and actin sites are too far away for the globular arms to shorten the muscle. This also makes it difficult for the muscle to produce a contraction.
Tight Muscles are More Susceptible to Injury
When a muscle is tight it is resistant to stretch so when a fast movement is made (which is common in sports or life for that matter) the muscle is more susceptible to tear injuries.
When muscles are overly tight they do not receive adequate blood flow which will result in painful trigger points also known as muscle knots.
Also, when one muscle is tight you will inevitably have one muscle that is inhibited or weak. Which means that those inhibited muscles will not do their job of stabilizing or protecting the joint as well resulting in an increased risk of injury to the joint and muscles.
How To Reduce Tightness for Optimal Performance!
To reduce tightness you can use self massage or self myofascial release with foam rollers or tennis balls for typically tight muscles like the pectorals, levator sccapulae, upper trapezius, low back muscles, hip flexors. Also stretch these muscles.
For learning relaxation while moving doing arm swings and leg swings and focusing on just letting your limbs just dangle. Also running in place but focusing on the shoulders and arms hanging loose as you run in place. For the legs hold on to a chair swing the legs forward and back and focus on just letting them swing with no contraction. Then shake the legs and feel the muscles of the thigh and hips just jiggle.
Manual therapy like massage is extremely helpful for chronic muscle tightness and adhesions that develop from muscles being tight for a long time. Stretching the muscle after decreasing adhesions help the adhesions become more moveable. Special stretching such as PNF stretching helps reset the muscle length in the brain and passive joint movement will help your body adapt to the new changes made to your muscles and joints.
 Matthew Snow is a Licensed Massage Therapist practicing in Greenwich, CT. If you would like schedule or make an appointment call (203) 660-0584 or email hello@h2tmuscleclinic.com[/fusion_builder_column][/fusion_builder_row][/fusion_builder_container]
Matthew Snow is a Licensed Massage Therapist practicing in Greenwich, CT. If you would like schedule or make an appointment call (203) 660-0584 or email hello@h2tmuscleclinic.com[/fusion_builder_column][/fusion_builder_row][/fusion_builder_container]